
There are many factors that affect binary options trading. Your result depends on the correctness of the strategy, risk management, your working capital. However, that’s not all. There are many factors that can change your prediction. These factors are taken into account in fundamental analysis: Reports, ratings, speeches of heads of financial institutions. In order to correctly understand where the information comes from, and how the news affects, you need to know who publishes these reports and news.
Some interesting facts about the most reputable rating agencies and their influence.
Rating agencies often publish their forecasts for oil prices, country ratings, etc. every time a rating agency such as S&P, Moody’s or Fitch comments, market volatility increases. We have analyzed the most reputable agencies and their impact on the market. I think you’ve noticed that every time binary options analysts tell us that a rating agency has assigned a rating to a certain company, and then the volatility on the currency price chart increases. At the same time, with increasing volatility, the trading volume in the market increases. All traders want to earn as much as possible in a short period of time, before entering the market due to revised ratings. Binary options have long been the main way to make money for many people. As for me, I would like to understand how to react to the data depending on the rating, and how to trade in such a way as to make a profit in this case.
- To track reporting, use the economic calendar
What ratings do agencies give?
When we talk about a rating attributed to a rating agency, we are referring to a credit rating. This rating helps when investors analyze the state of financial stability of a company or country. It helps to understand whether the company will be able to repay the borrowed funds, under what conditions this can happen, and whether the company will be able to pay the debts. It is logical to assume that the higher the rating, the better the conditions the company has for loans, and the more banks will agree to issue a loan, since, due to the high probability that the company will pay off the loan debt on time, which in turn means that the value of the company’s securities will grow. For example, Apple’s rating is AA+, which makes the company creditworthy in the US and France, but NOKIA’s credit rating is BB+, which makes the company less attractive than Apple, but more attractive to investors than Portugal, whose rating is BB.
The credit rating of a company or country is determined by a rating agency that specializes in assessing the creditworthiness and quality of guarantees issued by this unit. However, it should be noted that rating agencies use a methodology that initially assesses the probability of repayment of a possible loan taken by the user. Their methodology does not take into account the number of flow factors that may have a significant impact in the future, such as changes in market conditions or liquidity. Another important point of the rating agency is that they do not fully disclose their methodology and do not provide guarantees for calculations. Thus, their rating is more advisory than mandatory. Thus, we are dealing with the short-term impact of the rating on the market. Think of binary options and asset charts. How long can we observe a state of high volatility in the market?
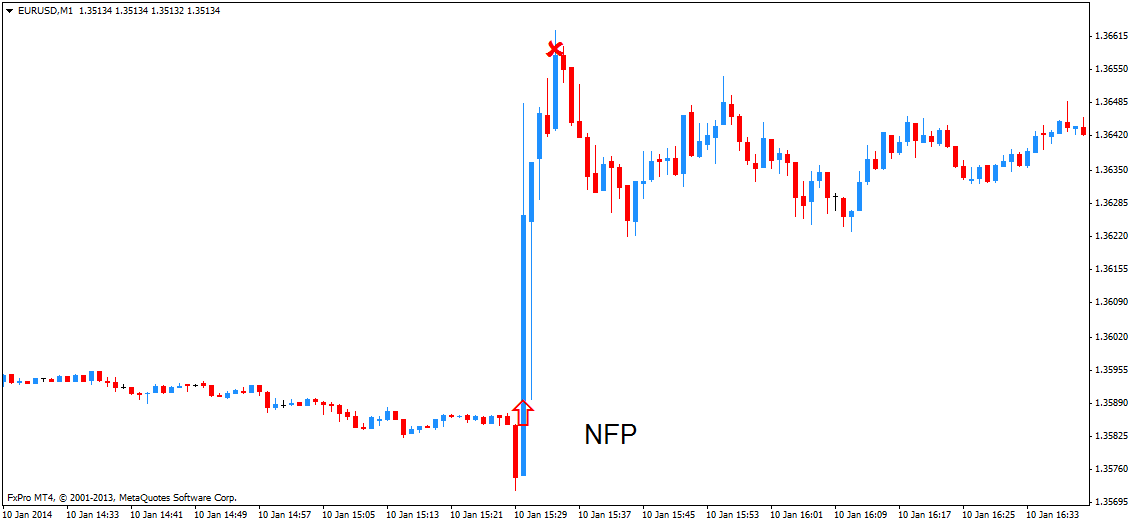
Panic goes away as long as the psychological factor works. The next day, the price is already adjusted based on market factors. So, it should be remembered that a credit rating is attributed for money, since it is a paid service bought by a company or country in order to be able to offer securities to a wider range of investors. At the same time, rating agencies monitor the status of the company, and not only just award a rating at a certain time, but also do it on the basis of cooperation. It should also be noted that the rating of the company cannot be higher than the rating of the country in which this company operates. Thus, a company can get a BB+ rating, but if it operates in a country that has a BB rating, then the company cannot get higher than this, it is also awarded an BB rating.
Another factor that affects the rating is its delay. It often happens that a rating is awarded at a certain time based on data obtained earlier, and not on what are the facts of the present. In 2008, the work of rating agencies was to confirm ratings. The agencies confirmed the consistently high ratings of companies such as AIG, Enron and Lehman Bros., but a month later these companies went bankrupt, which led to a crisis in the US financial markets. This is an explanation of why many investors do not trust rating agencies.
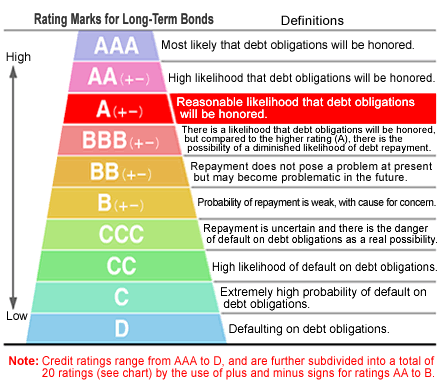 The rating shows the reliability of investments
The rating shows the reliability of investments
What are rating agencies?
There are about 100 rating agencies in the world. This includes both local and global agencies. Among the American rating agencies are Moody’s Investors Service, Standard & Poor’s and Fitch Ratings, which are the absolute leaders. Each rating agency uses its own methodologies in order to gain access to data on creditworthiness, gradation and assignment of ratings. However, in most cases, the assignments of the agencies are the same. The U.S. rating agency Standard & Poor’s is based in New York. Its revenue totals $2.45 billion last year alone. S&P assigns both national and international rankings. In order to determine the long-term rating, the S&P uses a spectrum of letters from “A” to “D”, as well as the symbols (+) or (-).
The agency uses letters to define the main categories and symbols, and letters and symbols to define indirect categories. Moody’s Investors Service, with annual profits of $3.3 billion, is also based in New York. It determines national and international rankings. Moody’s also uses letters, but does not have the letter “D” in its arsenal. Also, instead of the (+) and (-) symbols, Moody’s uses the numbers 1, 2, 3 to define indirect categories. These numbers indicate in which part of the category the designation is placed. Thus, BB1 assumes that the bond is at the top of the rating category. Fitch Ratings has two offices in New York and London.
The agency’s annual revenue is $1.12 billion. Fitch also uses the letters “A” to “E” to determine the rating. In graduation, the AAA rating is the highest, D is the default, and E is not enough information to assign a rating. E is assigned if the submitter has not provided sufficient documentation to calculate the rating.
Objectivity and influence of ratings
Rating agencies are important for the securities market. By establishing a company’s rating, they often determine the dynamics of the company’s securities movement in the market. A close ratio of assets is another asset for trading binary options, especially if its dynamics change. For example, as a result of the decline in oil prices, the value of securities of oil companies began to fall, which led to a decrease in tax payments to the budget and, consequently, an increase in the budget deficit. Thus, the rating agency Fitch downgraded the rating of Saudi Arabia due to a decrease in the price of oil, a decrease in the value of securities of manufacturing companies, and, as a result, an increase in the country’s budget deficit, which led to changes in the creditworthiness status. The rating reflects the attractiveness of the company for investors and lenders. However, the work of rating agencies is often associated with fraud, playing with factors such as objectivity, and this is often questionable.
A rating agency is a commercial company. The goal of every company is to make a profit. The agencies claim that their ratings are completely objective. But, as practice shows, this is not always the case. The strongest blow to the reputation of rating agencies was received in 2008. when they gave the maximum rating to companies that went bankrupt after a few months. In 2013, the rating agency S&P was criticized for downgrading the European Union. In August 2015, S&P downgraded the European Union again, resulting in a minimum position of 1.0880 for the EUR/USD currency pair.
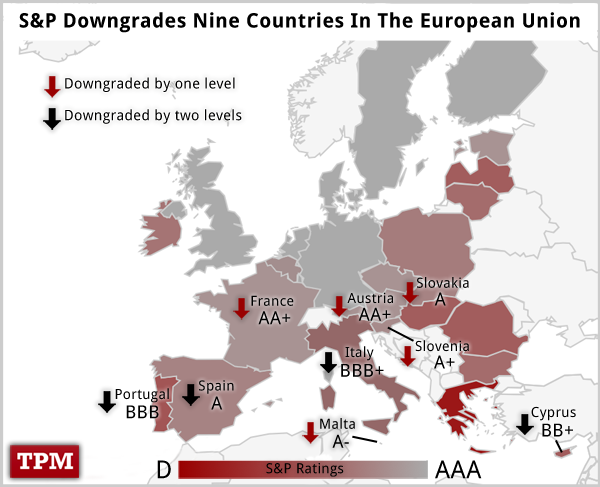
- In 2013, the rating agency S&P downgraded the rating of the European Union.
Moody’s Investors Service, Standard & Poor’s and Fitch Ratings account for 95% of the market. So they are a kind of monopoly in the ratings market. This means that there is no significant competition in the market, which may entail subjectivity of evaluation. Now, binary options traders use data on changes in the rating as short-term factors that affect the volatility of assets. Thus, the rating is a good opportunity to make a profit for a short period of panic in the market.
Tagged with: Binary Options Academy • Fundamental analysis • Learning how to trade binary


